3D Printing of Biomaterials
Oct 27, 2015
The use of 3D Printing dates back to 1980’s when Hull developed stereolithography. Hull was successful in integrating CAD with the computer for developing parts based on digital information. Presently, NASA launched 3D Printing machine towards International Space Station to develop parts in zero gravity. The Oak Ridge National Laboratory has built a complete car body through 3D Printing. Amongst all these advances, there is something happening in Healthcare too. It is the 3D Printing of Biomaterials.
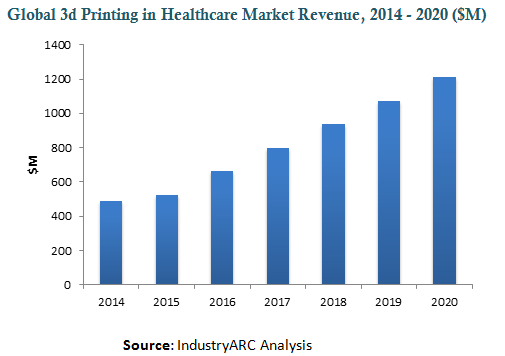
According to the research report by IndustryARC, the global value of 3D printing in Healthcare was $487 m in 2014. The market is estimated to grow at 18.3 %. Such growth is a combination of various applications of 3D printing in Healthcare. The 3D printing of biomaterials is one such application that is redefining the market dynamics. The vitality of saving patient lives remains unmatched. A small example of this is 3D printing of ears. According to statistics, 1 in every 8,000-10,000 children will develop the condition of Microtia. Microtia is a type of congenital deformity in which the ear is not completely developed. 3D printing can change the course of life for so many children.
The important question is that what is the need of 3D printing as the implants can be manufactured through Composite manufacturing too. The answer lies in the ability of 3D printing to provide immense freedom to the designer to develop innovative, complex and low-weight implants. An enormous amount of customization can be done through 3D printing. If we look at the dental practice, a dentist can replace a lost tooth in 6 minutes with the help of 3D printing. What has changed is that milling technique allows developing tooth with intricate details such as grooves and valleys. Even podiatrists are using 3D printing to develop custom foot insoles on the basis of 3D scan. Imagine a world where heart transplant can be completed in few hours. In the next 20 years, we can witness a 3D printed heart functioning properly without rejection by the body. The scientists are trying to develop heart through 3D printing by using the human body cells. The researchers are trying to explore new avenues such as Organ printing and it will be the next big thing in Healthcare.
The global 3D printing in healthcare market in 2014 was dominated by the Americas due to increased adoption of 3D printing technologies and increased investments. Europe is the second major shareholder of global 3D printing in healthcare market next to Americas. Europe market is estimated to grow at a great pace due to significant developments such as mergers and acquisitions and remarkable investments by government in 3D technologies. Asia-Pacific is also estimated to experience remarkable growth in this market, exhibiting a CAGR of 23.5% over the forecast period. Even though, Asia-Pacific’s 3D printing in healthcare market share is lower than that of Europe at present, and it is estimated to have significant market potential in future due to increasing populations and applications of 3D printing in implants and surgeries.
3D Printing in Biomaterials is going to gain traction in the future with personalized medicine at the helm. The customization of nutritional products and organs will help in providing better treatment and save numerous lives. The concept of In situ printing will enable researchers to develop complex organs such as kidneys and liver. It is the ideal time to take a leap forward for the betterment of human lives and mankind and 3D printing is going to help us in doing that.
Source: 3DPRINTING.COM